Historical Review of the Agua Salud River Experimental Watershed
During the period of the construction of the Canal by the Americans, it was believed that the failure of the […]
During the period of the construction of the Canal by the Americans, it was believed that the failure of the French was to ignore the power of the mighty Chagres River. The collection of data on this torrent and its tributaries and the making of forecasts on the availability of water to operate the Canal, constituted the main responsibilities of the Directorate of Meteorology and Hydraulics of the Rivers of the Isthmian Canal Commission (1907), which is the precursor of what is today the Water Division of the Canal.
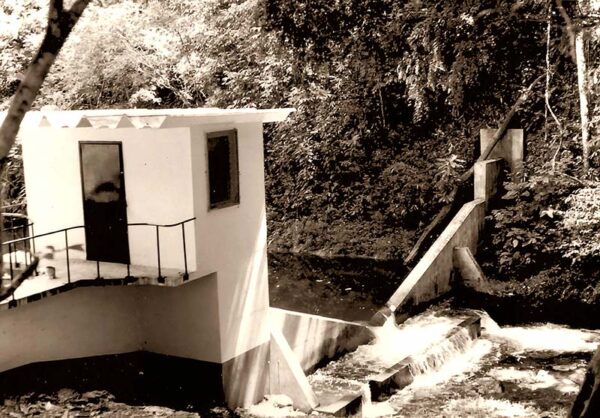

That is why, since its inception, the Canal has used everything from machetes and horses to the most advanced computerized technology to reach remote locations, where it can monitor the amount of water available for the production of the waterworks, the navigation of its channel, and at the same time maintain an effective flow control program.
At the recommendation of the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Mobile District, the Panama Canal initiated a project in 1979, managed by the then Canal Meteorological and Hydrographic Branch, to establish and record a relationship between rainfall and runoff (the flow of water) discharged into the reservoirs of the Canal Watershed.
The project was based on choosing an area named as the experimental Watershed, where three weirs (water gauging devices) would be constructed in three microwatersheds with similar hydrological characteristics, but with different land use. These were designed to ensure the flow of water in open channels and installed in rivers that flow into Gatun Lake. Each spillway would have a device to record the rise and fall of the water. This experimental watershed was created for the purpose of determining threshold values for a set of hydrometeorological parameters (soil moisture, evapotranspiration, among others) that would be used as inputs for a computerized hydrological flow forecasting model, to calibrate the model for later use in the flow forecasting program, and to study the effects of deforestation on the water balance and regulation of the area. The experimental Watershed would also be used by other organizations for environmental, erosion, and water quality studies.
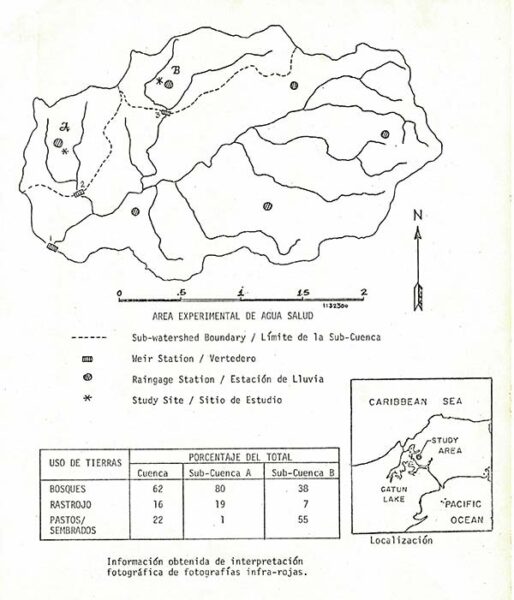
The chosen area
The project was established in the Agua Salud River area. This 20 square kilometer globe is representative of the Canal Watershed because it is made up of three distinct vegetation covers found in the area: forested, partially forested, and deforested, with areas with bare soils.
Located 16 kilometers northeast of Gamboa, the area presented favorable characteristics, such as:
- Accessible by road.
- It has characteristics that are representative of the Canal Watershed.
- It has a sufficiently dense drainage network.
- It is small enough to allow the installation of a data network at a reasonable cost.
- It includes forests and agricultural land, typical of the Gatun Reservoir Watershed.
The Construction
The project was built in 1979 at a cost of $155,000.
Mosquitoes, snakes, ants whose bites produced fevers, extreme heat, and places within the experimental Watershed that could only be reached by helicopter, were some of the challenges in constructing the spillways. These reinforced concrete structures measure the flow of water in open channels, built from one side of the river or creek to the other, where water flows over it, usually through a rectangular or V-shaped cutout at the top. A charting device is installed along with the spillway to record the rise and fall of the water surface for a given period. The men who participated in the construction lived and worked under the most inhospitable conditions. They built sleeping huts and had to mix the concrete by hand and handle the concrete buckets with ropes.
Hydrometeorological measurements
In the Agua Salud River Experimental Watershed, in addition to measurements of runoff at the spillways, representative rainfall evaluations were also carried out in the Watershed. This measurement was carried out with six rain collectors located on the roof of wooden instrumentation huts designed and built by the staff of the hydrometeorology department and transported to the site by helicopters.
Data were collected on evapotranspiration, which is evaporation from the soil and from the surface covered by plants and transpiration from plant leaves, using spherical black and white porcelain-porous spherical sensors, known as Livingstone atmometers. Wind, temperature and relative humidity measurements were also made.
The experimental Watershed was put into operation in 1979 and by 1981, the instruments placed in it were collecting information on rainfall, streamflow, soil moisture and evaporation that would later be used to establish the parameters by means of computers with the technology of the time.
The information collected
The information from the Agua Salud River Experimental Watershed is vast. They are studies, measurements, results, statistics, reports and forms that were compiled between 1979 and 1984. All this information rests in the Roberto F. Chiari Library and is accessible to the general public Monday through Friday from 7:00 a.m. to 3:30 p.m. Many of these documents can be viewed from the library’s online catalog. Access this link and enter the word “Agua Salud” in the catalog search engine.
Bibliography
- Corelli, J. (1988). Agua Salud River Watershed Study. Panamá: Panama Canal Commission.
- Meriwether, J. (1981, October 1). Vigilantes de las aguas del Canal. Panama Canal Review, pp. 10-19.
- Panama Canal Company. (1979). Annual Report. Fiscal year ended september 30, 1979. Panama: Panama Canal Company.
- Wong, J., & Corelli, J. (198-). Area Experimental de Agua Salud. Panama: Panama Canal Commission.